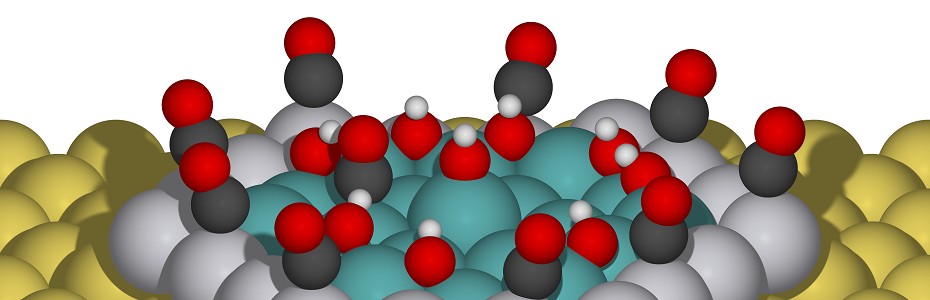
L-Proline Catalyzed Synthesis of Novel 5-{[2-(2-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)quinolin] methylene}-2,4-dione Derivatives
Author(s): S.S. Praveen Kumar Darsi, K. Shiva Kumar, B. Rama Devi, A. Naidu and P.K. Dubey
Affiliation: Department of Chemistry, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad College of Engineering, Kukatpally, Hyderabad (A.P), India-500 085.
Abstract
L-proline is found to be an efficient catalyst for the Knoevenagel condensation of 2-chloroquinoline-3- carboxaldehyde 1a-c with an active methylene compound i.e., 2,4-thazolidinedione 2 in IPA affording novel substituted olefins 3a-c. The latter products reacted with N-substituted-3-phenylpiperazine 4a-c in the presence of KF in DMF to afford the corresponding 5-{[2-(2-phenylpiperazin-1-yl)quinolin]methylene}-2,4-dione derivatives 6a-i. Alternatively, 6ai were also synthesized from another reaction sequence 1 → 5 → 6. The structures of the synthesized compounds have been established on the basis of spectral and analytical data.
Synthesis of 3-substituted Coumarins: An Efficient Green Approach Using L-proline as Catalyst in Triethanolamine Medium
Author(s): Devulapally Srikrishna, Syed Tasqeeruddin and Pramod Kumar Dubey
Affiliation: Department of Chemistry, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabad College of Engineering, Kukatpally, Hyderabad, India – 500085.
Abstract
3-Substituted coumarins were synthesized very efficiently, using Knoevenagel method from salicylaldehydes 1 and active methylene compounds 2 under green conditions. The effect of catalyst and solvent on this condensation was studied. L-proline was found to be the best catalyst and triethanolamine the best reaction medium for this reaction.
Synthesis, Characterization, Antibacterial and Free Radical Scavenging Activities of Some New 1,2,4-triazole Schiff Bases and Mannich Bases
Author(s): Kooi-Mow Sim, Siew-Theng Loo and Kah-Cheng Teo
Affiliation: Department of Chemical Science, Faculty of Science, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Jalan Universiti, Bandar Barat, 31900 Kampar, Perak, Malaysia and Centre for Biodiversity Research, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Jalan Universiti, Bandar Barat, 31900 Kampar, Perak, Malaysia.
Abstract
The synthesis of a series of 1,2,4-triazole Schiff bases and Mannich bases incorporating an indole moiety is described. The triazole Schiff bases were synthesized from 4-amino-3-mercapto-5-[(1H-indol-3-yl)methyl]-1,2,4-triazole on treatment with a series of arylaldehyde in presence of (+)-tartaric acid as an acidic catalyst. The triazole Schiff bases are further condensed with piperidine and formaldehyde to yield the corresponding series of Mannich bases. The structures of Schiff bases and Mannich bases were established by IR, NMR and mass spectral data. All the synthesized compounds were screened for their antibacterial and free radical scavenging activities. Schiff base 2d comprising of dichloro substitution exhibited promising antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis spizizenni, Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus at MIC 7.81 μ g/ml. Mannich bases demonstrated weak free radical scavenging activity when compared to their Schiff base counterparts.
Ultrasonic and Microwave Assisted Synthesis of Nitrogen-Containing Derivatives of Juglone as Potential Antibacterial Agents
Author(s): Lluvia Itzel Lopez-Lopez, Jesus Javier Vaquera Garcia, Aide Saenz-Galindo and Sonia Yesenia Silva-Belmares
Affiliation: Department of Organic Chemistry, School of Chemistry, Universidad Autonoma de Coahuila, Saltillo, 25280, Coahuila, Mexico.
Abstract
Ultrasound and microwave assisted expedient synthesis of potential antibacterial compounds, 2-(anilino)-5- hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives 3a-c and 5-hydroxybenzo[f]indole-4,9-dione derivatives 8a-c and 10- hydroxybenzo[b]carbazole-6,11-dione derivatives 9a-c have been developed. For the preparation of 3a-c derivatives the methods Room Temperature Synthesis (RTS), Conventional Heating Synthesis (CHS) and Ultrasound Assisted Synthesis (UAS) were performed. In addition, the Conventional Synthesis (CS) and Microwave Assisted Synthesis (MAS) were used for 8a-c and 9a-c derivatives. UAS and MAS showed the best results and are considered green alternatives of synthesis. In general, the yields obtained were good to excellent (58 to 93%). In addition, antibacterial activity against five bacterial strains was tested, showing bacteriostatic activity at lower concentrations and greater bactericidal against Gram negative strains. The compounds carrying chlorine atoms at 2 and 4 positions on the phenyl ring were the most active. The results obtained indicate that the 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives presented here have promising use as antibacterial agents. A reaction mechanism is also proposed.
Laccase Inhibiting Activity of Some Coumarin Derivatives
Author(s): Marina Ti sma, Maja Molnar, Marija Skarica, Milan Cacic and Bruno Zelic
Affiliation: J.J. Strossmayer University of Osijek, Faculty of Food Technology Osijek, F. Kuha ca 20, HR-31000 Osijek, Croatia.
Abstract
Seven coumarin derivatives were screened for their inhibitory effect on laccase utilizing ABTS and L-DOPA as substrates. 2-[(4-Methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl)oxy]acetic acid (E)-2-[(dihydroxyphenyl)methylene]hydrazides were proven to be stronger inhibitors than corresponding thiosemicarbazides when ABTS [2,2′-azinobis(3- ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)] was used as a substrate. In kinetic experiments mixed type inhibition was determined for 2-[(4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-1-benzopyran-7-yl)oxy]acetic acid (E)-2-[(2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)methylene]hydrazide and (E)-2-[(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methylene]hydrazide. In reaction of L-DOPA (L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) oxidation catalyzed by laccase none of the tested compounds has shown inhibitory effect.
Efficient Chemical Synthesis of a Scutellarein Derivative Containing Morpholine Ring
Author(s): Qian-Ping Shi, Zhi-Hao Shi, Nian-Guang Li, Yu-Ping Tang, Hao- Tang, Wei Zhang, Min-Zhe Shen, Ze-Xi Dong, Peng-Xuan Zhang, Jian-Ping Yang and Jin-Ao Duan
Affiliation: Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Chinese Medicinal Resources Industrialization, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, P.R. China.
Abstract
Scutellarin (1) [5,6-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-1-benzopyran-7-yl β -D-glucopyranosiduronic acid] is very effective in the clinical treatment of cerebral infarction and coronary heart disease in China. Pharmacokinetic studies showed that scutellarin (1) is readily metabolized to scutellarein (2) [5,6,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1- benzopyran-4-one] in the intestine by β -glucuronide enzyme prior to absorption. In order to improve the biological activity of scutellarin (1), our group has previously synthesized many scutellarin derivatives based on their in vivo metabolic mechanism. The results showed that morpholine ring substituted at C-7 or C-8 position induced better antioxidant activity, water solubility and anticoagulant activity compared to scutellarin (1). In this paper, an efficient synthetic method for the construction of 5,6,7-trihydroxy-2-[4-[2-(4-morpholinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (5) is reported. This synthetic route will facilitate the synthesis of scutellarein derivatives containing an amine side chain at the C- 4′ position.